Automating Jupyter Notebooks with Papermill
Authors: Ayush Alhat, Guransh Saran, Himani Goel
Date: February 25, 2025
Introduction
In the world of data science and automation, running Jupyter Notebooks manually can be repetitive and time-consuming, especially when working with different datasets or parameters. This is where Papermill comes in!
Papermill is an open-source Python library that allows you to:
- Parameterize Jupyter Notebooks (pass different values without editing the code).
- Execute Notebooks programmatically (automate repetitive tasks).
- Track and log executions (useful for debugging and reproducibility).
With Papermill, you can efficiently run the same notebook multiple times with different inputs, making it a powerful tool for data pipelines, automated reporting, and machine learning workflows.
Installation & Setup of Papermill
1. Install Papermill using pip
Papermill is a Python library, so you can install it using pip:
pip install papermill
2. Verify the Installation
After installation, check if Papermill is installed correctly by running:
papermill --help
3. Install Jupyter Notebook (If Not Already Installed)
Papermill works with Jupyter Notebooks, so make sure Jupyter is installed:
pip install notebook
4. Running a Jupyter Notebook with Papermill
Once installed, you can use Papermill to execute a notebook from the command line:
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb -p param_name param_value
Example: Running a notebook while setting a parameter
papermill my_notebook.ipynb output.ipynb -p num_epochs 10
5. Using Papermill in a Python Script
You can also run Papermill inside a Python script:
import papermill as pm
pm.execute_notebook(
"input_notebook.ipynb",
"output_notebook.ipynb",
parameters={"num_epochs": 10, "learning_rate": 0.01}
)
Now you have Papermill installed and ready to use!
Key Features
Papermill is a powerful tool that allows for automation and parameterization of Jupyter Notebooks. Below are its key functionalities:
1. Parameterization of Notebooks
What it does: Papermill allows users to pass parameters into a Jupyter Notebook at runtime, enabling dynamic execution with different inputs.
How it works: A notebook can contain a specially tagged cell (usually marked as "parameters" in Jupyter) where variables are defined. Papermill can override these variables at execution time.
Why it's useful:
- Eliminates the need for manually editing a notebook to change input values.
- Enables dynamic workflows and experimentation with different configurations.
- Supports automation in machine learning and data processing pipelines.
Example Usage:
# This cell is tagged as "parameters" in Jupyter
alpha = 0.1
beta = 0.5
Running the notebook with different parameters using Papermill:
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb -p alpha 0.2 -p beta 0.7
2. Execution of Notebooks
What it does: Papermill automates the execution of Jupyter Notebooks programmatically.
How it works: It runs the notebook in a clean execution environment, executing each cell sequentially from top to bottom.
Why it's useful:
- Automates repetitive analysis tasks.
- Allows scheduling and running notebooks in batch jobs.
- Ensures reproducibility and consistency in data workflows.
Example Usage:
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb
3. Recording Notebook Metadata
What it does: Papermill records execution metadata, including runtime parameters, execution duration, and timestamps.
How it works: When a notebook is executed, metadata is embedded in its JSON structure. This metadata can be inspected later to track how a notebook was executed.
Why it's useful:
- Helps with debugging and understanding past executions.
- Tracks parameter values used in different runs.
- Enables logging and monitoring of notebook executions.
4. Error Handling and Checkpointing
What it does: Papermill captures errors that occur during execution and preserves partial execution states.
How it works: If an error occurs, Papermill stops execution but keeps the notebook intact with executed cells up to the failure point.
Why it's useful:
- Provides visibility into execution failures without losing progress.
- Useful for debugging long-running jobs.
- Allows restarting from the last successful cell.
Example Usage:
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb --log-output
5. Integration with Data Pipelines
What it does: Papermill integrates with workflow orchestration tools like Apache Airflow, Kubeflow, and AWS Step Functions.
How it works: It allows notebooks to be treated as reusable components in larger data pipelines.
Why it's useful:
- Enables seamless automation and scheduling of data science workflows.
- Supports cloud-based execution in platforms like AWS, GCP, and Azure.
- Works well with CI/CD pipelines in machine learning.
6. Storage and Remote Execution
What it does: Papermill supports reading and writing notebooks from various storage systems and executing notebooks on remote servers.
How it works: It can read and write notebooks from:
- Local files
- S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service)
- Google Cloud Storage
- Azure Blob Storage
- Databases
It can also execute notebooks remotely on:
- JupyterHub
- Kubernetes
- Cloud-based environments
Why it's useful:
- Enables scalable execution in distributed systems.
- Supports cloud-based data science workflows.
Example Usage:
papermill s3://my-bucket/input_notebook.ipynb s3://my-bucket/output_notebook.ipynb
7. Output and Result Management
What it does: Papermill saves executed notebooks with results and outputs.
How it works: After execution, the modified notebook is stored with:
- Updated parameter values
- Executed outputs (charts, tables, logs)
- Metadata
Why it's useful:
- Keeps a historical record of different executions.
- Enables versioning and comparison of results.
Code Examples: Working with Papermill
Below is an example of how to use Papermill for automating Jupyter Notebooks.
Firstly ensure you have papermill installed by running the following command in your terminal:
pip install papermill
Now create a jupyter notebook and import papermill as shown below:
Next, create a cell in the notebook and tag it as "parameters" to define the variables you want to parameterize:
Write the main code in the notebook, using the parameters defined earlier, for example:
Add this code at the end of your notebook to log all different parameter values and the results obtained into one CSV file. This is done because the output notebook will be overwritten and will only contain the last executed parameters.
Create an output notebook and then finally, execute the input notebook with different parameter values by running the following command in your terminal:
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb -p alpha {value1} -p beta {value2}
Attached below are screenshots of what your output notebook and CSV file will look like after running the commands:
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb -p alpha 1 -p beta 1
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb -p alpha 2 -p beta 2
papermill input_notebook.ipynb output_notebook.ipynb -p alpha 3 -p beta 3
Output Notebook
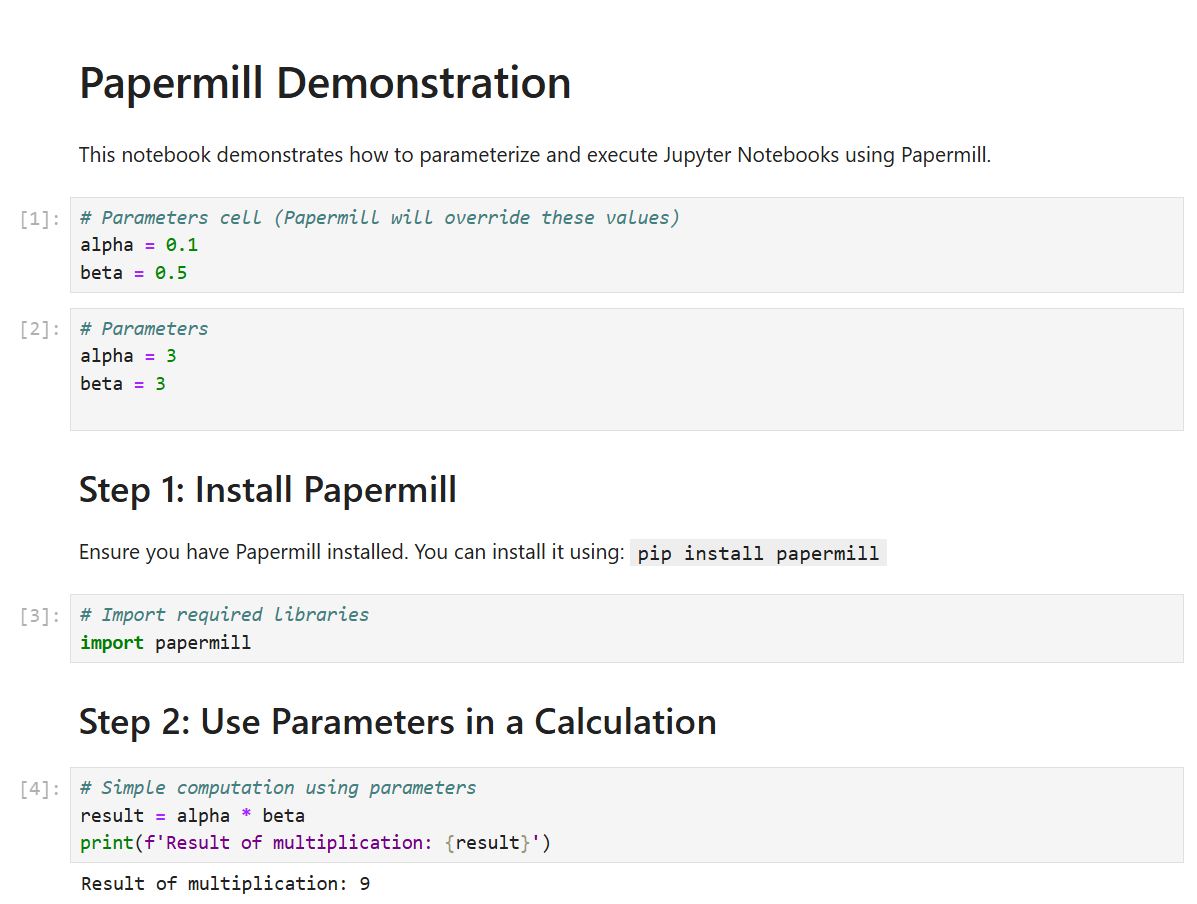
CSV File

Screenshots
Below are some screenshots to illustrate key functionalities of Papermill.
1. Running Papermill in Command Line
Input Notebook: papermill_demo.ipynb
Output Notebook: output_notebook.ipynb
Parameters: alpha, beta

This shows Papermill executing a Jupyter Notebook with parameters.
2. Viewing Execution Metadata

Papermill automatically logs execution details for tracking and debugging.
3. Parameterization of Notebooks
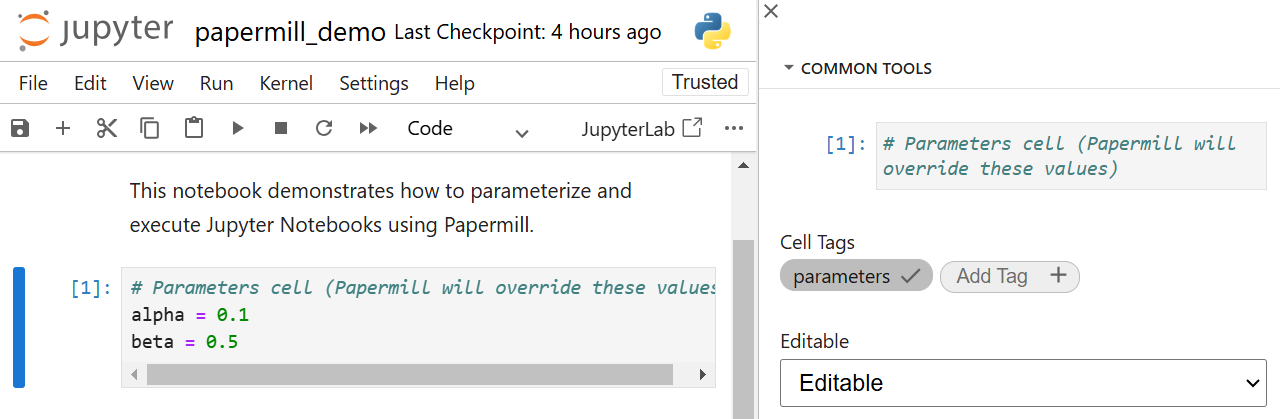
This shows a Jupyter Notebook cell tagged as "parameters" with variables defined.
4. Error Handling and Checkpointing
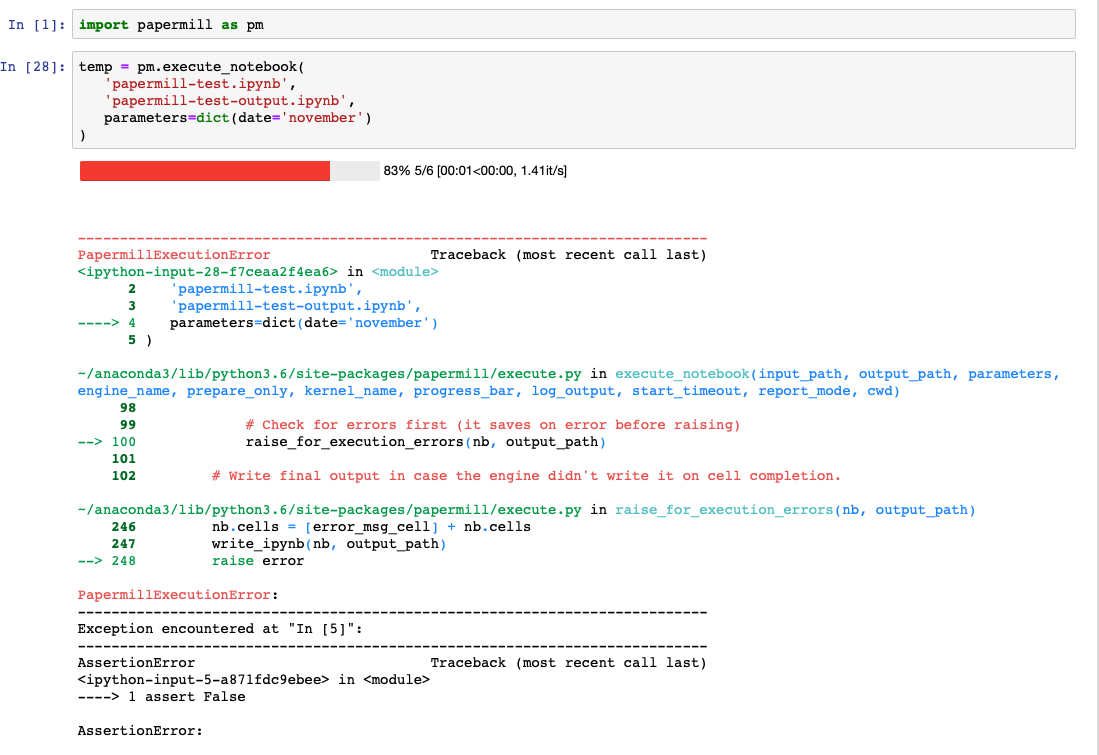
This shows a notebook with an error during execution and the cells executed up to the failure point.
5. Output and Result Management

This shows an executed notebook with updated parameter values and outputs.
Use Cases: Where is Papermill Useful?
Papermill is widely used in various domains to automate Jupyter Notebooks.
- Data Science:
Papermill allows data scientists to run the same notebook with different datasets by passing parameters at runtime. This helps in comparing results across multiple datasets without manually changing the notebook.
- Machine Learning:
Papermill can be used to automate the process of hyperparameter tuning by running the notebook multiple times with different parameter values. This is useful for training machine learning models with various configurations to find the best performing model.
- Reporting & Dashboards:
Papermill can automate the generation of reports by running notebooks with updated data. This is useful for creating daily, weekly, or monthly reports without manual intervention.
- ETL Pipelines:
Papermill can be integrated into ETL pipelines to automate the process of extracting data from sources, transforming it, and loading it into databases or data warehouses. This ensures that data processing tasks are consistent and reproducible.
- Cloud Deployments:
Papermill supports execution on cloud platforms, making it easy to run notebooks in cloud-based environments. This is useful for leveraging cloud resources for scalable and distributed data processing.
These use cases highlight the versatility of Papermill in automating and parameterizing Jupyter Notebooks, making it a valuable tool for data scientists, engineers, and analysts.
Conclusion
Papermill is a powerful and versatile tool that significantly enhances the capabilities of Jupyter Notebooks. By enabling parameterization, automated execution, and detailed execution tracking, Papermill streamlines workflows and boosts productivity for data scientists, engineers, and analysts.
Whether you are running experiments with different datasets, automating machine learning model training, generating periodic reports, or integrating notebooks into complex data pipelines, Papermill provides the flexibility and scalability needed to handle these tasks efficiently.
With its support for cloud deployments and various storage systems, Papermill also facilitates seamless integration into modern data science and machine learning environments. By leveraging Papermill, you can save time, ensure reproducibility, and scale your workflows effectively.
We hope this blog has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Papermill's key features and use cases. Start exploring Papermill today and unlock the full potential of your Jupyter Notebooks!
References & Further Reading





